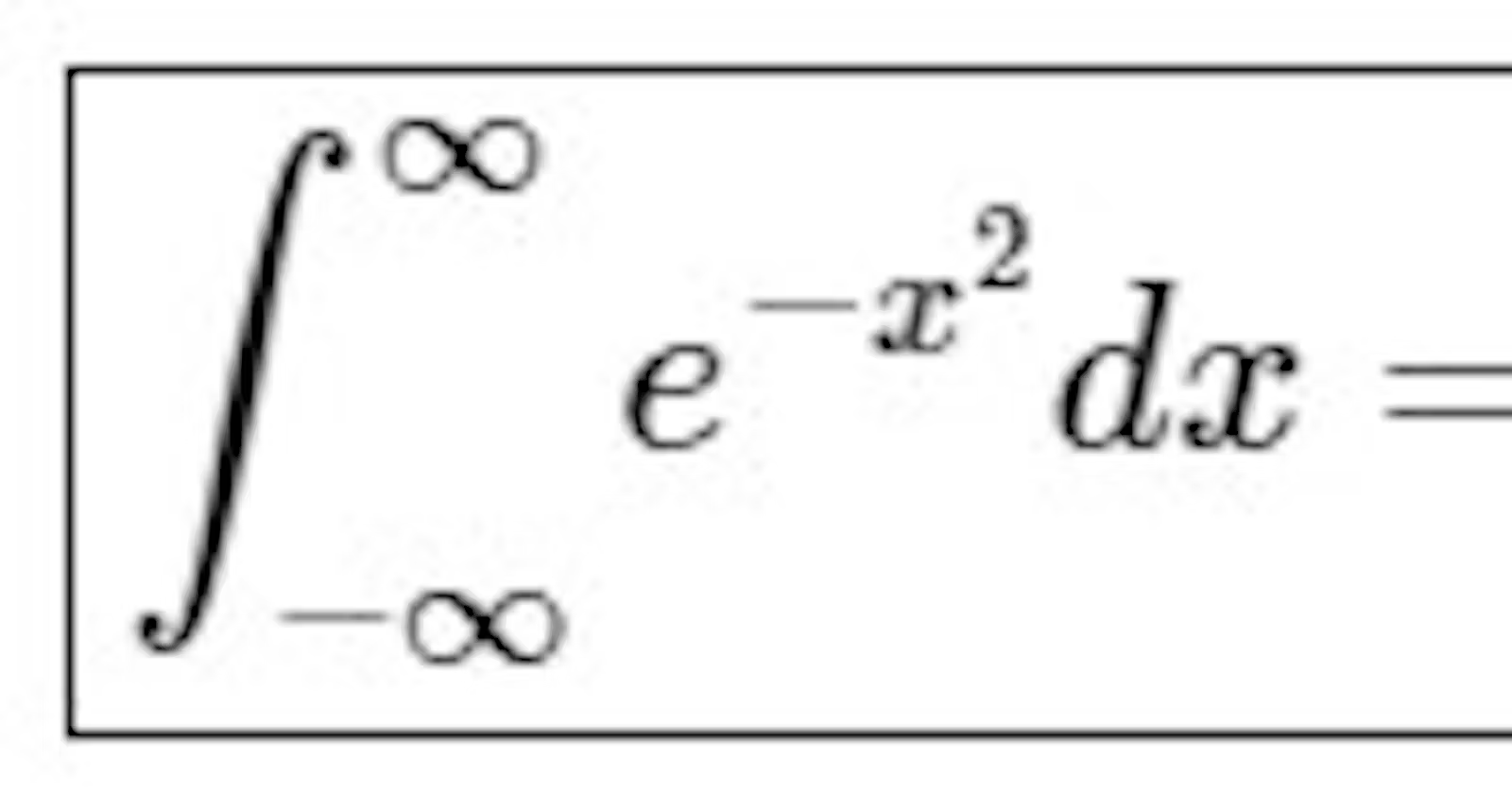The definite integral of over the entire real line does have a beautiful result involving :
Consider the square of the integral: Let , then
Use Fubini’s theorem to convert to a double integral:
Simplify and convert to polar coordinates:
Now, convert to polar coordinates:
So
Evaluate the double integral: First, evaluate the inner integral with respect to . We can use a simple substitution: let
Now, substitute this back into the double integral:
Take the square root . So we have proven that: